July 14 2016
Comparing Electric Vehicles
There are 17 different models of Electric Vehicle available in Canada. 7 Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) and 10 Plug in Hybrids (PHEV). No two are the same. Battery sizes vary as does the range available from a fully charged battery. They come in a range of sizes and a variety of costs. The Mitsubish MiEV is an urban commuter car which has a list price of below $30,000 whereas the BMW i8 delivers sports car performance at a cost of over $150,000.
All electric vehicles available in Canada are described on the Plug'n'Drive website which is an invaluable resource for EV customers.
So with so many choices – how can these EVs be compared?
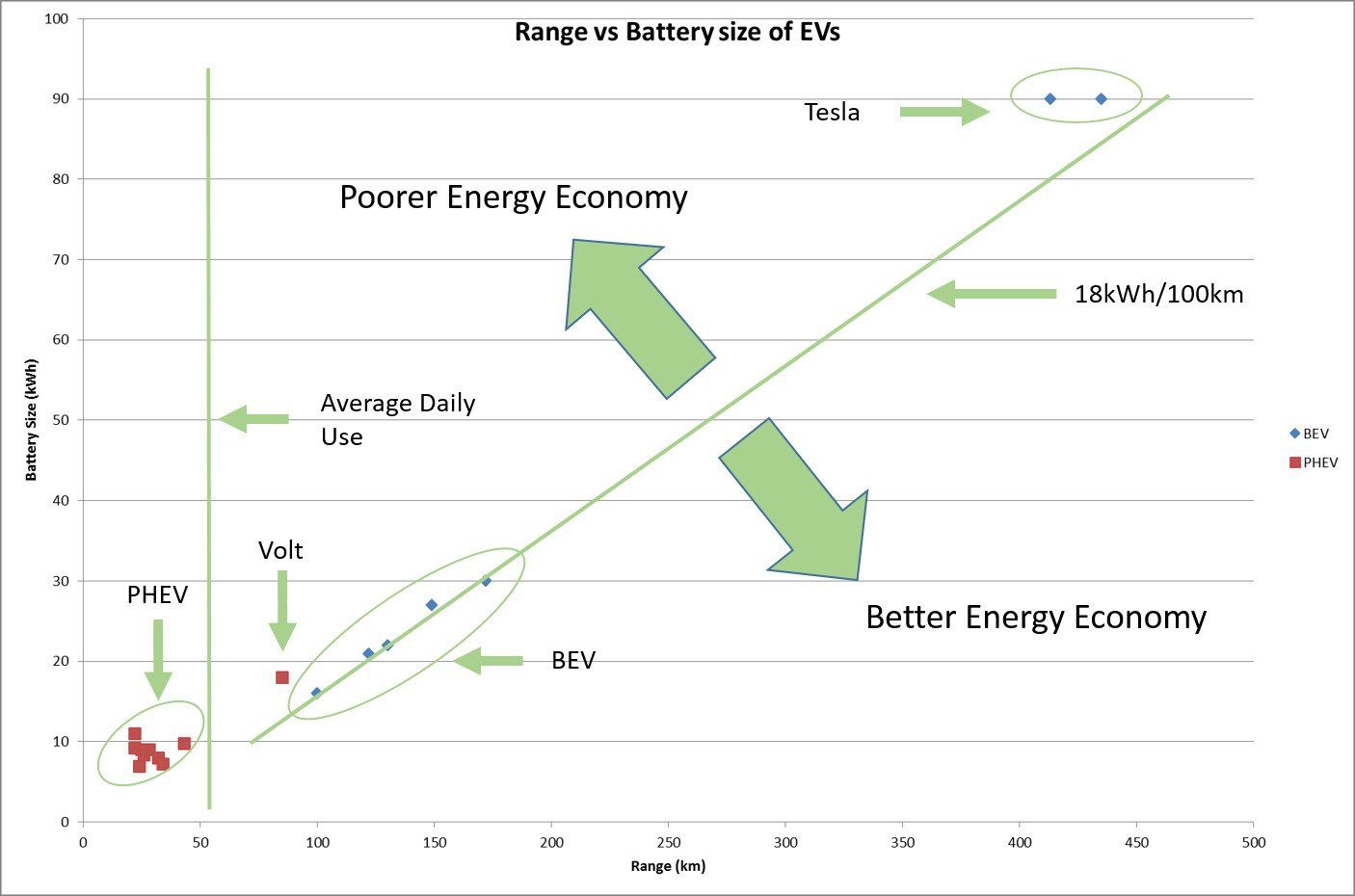
The chart below plots the range of each vehicle (while driven electrically) against the size of the installed battery pack.
The PHEVs with small battery packs offer a small electrical range (typically between 25km and 35km). After this, they revert to their conventional engine. There is no range anxiety with these vehicles but a user who drives the national average daily mileage of 50km will not be able to drive purely on battery power. The exception to this is the Chevrolet Volt which has an electrical range of 85km. This is achieved by the simple expedient of installing a large battery: 18kWh – double the average PHEV battery size.
BatteryElectric Vehicles all have a similar consumption figure of around 18kWh per 100km. Range varies from 100km for the Mitsubishi MiEV to 172km for the Nissan Leaf. The achievable range is directly connected to the size of the installed battery pack.
And then, in a class of their own, are the Teslas (Model S and Model X) They offer a range of over 400km on a single charge. As with the other BEVs the extended range is achieved by installing a much larger battery. Tesla batteries are typically 90kWh each (over 5 times as large as the MiEV)